Problem Set 10: Spectrometry#
A laser system is designed to fabricate fiber Bragg gratings. In order to create in expensive gratings they are fabricated at the same time as the optical fiber (called draw tower gratings). This requires the laser system to be redirected by mirrors. The system consists of a laser with a wavelength of \(\lambda = 244 nm\), routing mirrors, and a spatial filter that consists of two lenses and a pin hole. The initial irradiance of the laser beam is \(I_1=10^4 \exp{\left(-\left(\frac{r}{10^{-3}}\right)^2\right)} W/m^2\). Assume that with perfectly clean mirror the irradiance pattern at the first lens is the same as the irradiance pattern at the laser. The focal length of the first lens is \(f_1=10mm\). The second lens is chosen such that the change in the irradiance over the grating length of D=10mm is 20%.
What is the normalized irradiance of the final beam (labeled as \(I_2\) on Fig. 11) without the pin hole?
What is the focal length of the second lens?
If the mirrors add a periodic change in the intensity resulting in an electric field of \(E_1=\left[\exp{\left(-\frac{1}{2}\left(\frac{r}{10^{-3}}\right)^2\right)}\right]\left[1+0.5\sin{\left(10^4x\right)}\right]\), what is the normalized electric field pattern at the grating?
What is the diameter of the pinhole that performs the spatial filtering? Choose the diameter of the pinhole such that 90% of the sinusoidal variation is blocked.
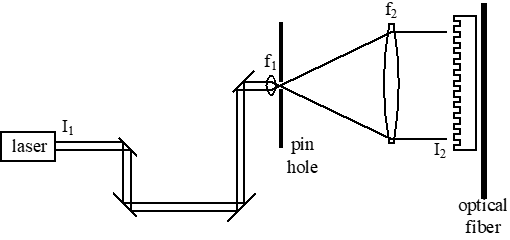
Fig. 11 Bragg grating fabrication scheme.#
A common spectrometer is the Czerny-Turner spectrometer configuration. We can model this as a uniform beam normally incident onto a grating. The diffracted beam at an angle of 45 degrees is then focused onto a CCD array by another perfect lens (see Fig. 12). The diameter of the beam is D=100mm and the focal lengths of the lenses are f=200mm. The CCD array has 3000 pixels with a pixel size of \(7 \mu m\) (see http://www.newport.com/Oriel-Linespec-Gated-Linear-CCD-Array-Detector/375933/1033/catalog.aspx). Use a central wavelength of 500 nm.
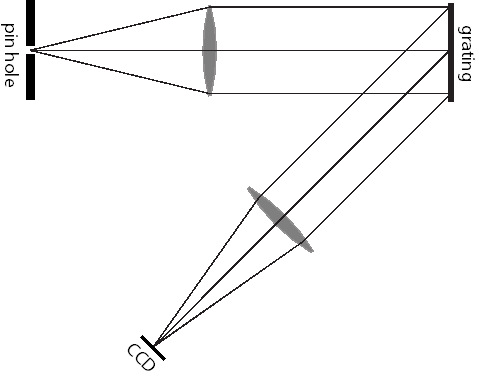
Fig. 12 Spectrometry setup.#
- What is the wavelength resolution of the spectrometer? (This is the wavelength band across a single pixel.)
- What is the maximum wavelength range of the spectrometer? (This is the wavelength band across the entire CCD.)
Solutions
Problem 1
Some hidden toggle content!
Problem 2
Some hidden toggle content!
