Problem Set 3: Cameras#
The following web site gives the specifications for the Nikon Coolpix L22. This is the camera that the department owns. This camera is called a simple point and shoot camera. On the specifications the focal lengths are actually “35 mm equivalent focal lengths” (see Wikipedia: 35mm equivalent focal length). See here for sensor size specifications.
- What is the pixel dimension?
- What are the actual focal lengths of the camera?
- What is the total field of view (FOV) for the camera when it is at its most wide angle zoom limit?
- What is the total field of view (FOV) for the camera when it is at its most telephoto zoom limit?
- What is the pixel size of an image at a distance of 50m using the most telephoto zoom?
You are designing a camera that is used to read the license plate of vehicles that run red lights. The distance between the camera and the license plate is 10m. For your information the letters on a license plate are 60mm tall. To be able to distinguish between the letters and number (i.e. B and 8) you need at least 20 pixels across. This means that your camera needs to have an image pixel size of 60/20=3mm. The total field of view of the entire image needs to be able to image the entire road. So the entire image size needs to be 3.4 m. Your design needs to use a commercially available CCD sensor array. The sensor array that you need to use is called a 1/3.6” CCD, which has a size of 4mm X 3mm. To keep the cost down you should use the fewest number of CCD pixel elements as possible. Be sure to include the following.
- A description of your design.
- A layout of your camera design. You should only have a single lens. (You can assume that your lens is perfect. You just need to specify the focal length and position of the lens relative to the CCD.)
An optical system is designed with two lenses. The first lens is biconvex with a focal length of \(f=20mm\) and a diameter of 20mm. The second lens is biconcave with a focal length of \(f=-20mm\) and a diameter of 40mm. The separation of the lenses is 20mm. A 10mm aperture is placed 30mm in front of the first lens. A 20mm tall object is located 60mm in front of the first lenses. Fig. 4 shows a scale drawing of the optical system. Assume that all light that does not pass through each lens is blocked. This aperture is shown as the black box around the lens system. Assume that the paraxial approximation is valid.
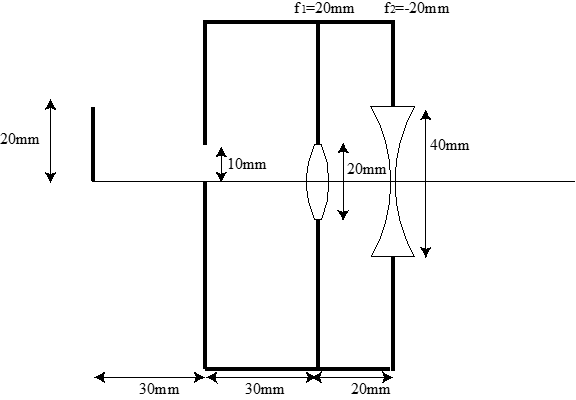
Fig. 4 Lens system with aperture.#
- What is the location of the image?
- What is the size of the image?
- Draw rays on {numref}`aperture-fig` that show the maximum extent of area used for each lens.
- What fractional height of each lens has optical light passing through it that contributes to the image?
You will be designing and analyzing a zoom lens made using perfect lenses. Your zoom lens should have a focus range of \(7mm \lt f \lt 26mm\). Read over the design section on Wikipedia.
- What are the focal lengths of the 4 lenses?
- Make a plot of the system at the two extremes (f=7mm and f=26mm).
Solutions
Problem 1
Some hidden toggle content!
Problem 2
Some hidden toggle content!
Problem 3
Some hidden toggle content!
Problem 4
Some hidden toggle content!
